5-MAPB vs. MDMA: Key Differences for Research
5-MAPB vs. MDMA: Key Differences for Research
When comparing 5-MAPB vs MDMA, researchers are often interested in how subtle structural changes lead to different outcomes in laboratory studies. Both compounds share a similar backbone as entactogenic stimulants, yet they differ in chemical composition, pharmacological activity, and research applications. This comparison provides valuable insight for scientists studying novel psychoactive substances.
What Is 5-MAPB?
5-MAPB, short for 5-(2-methylaminopropyl)benzofuran, is a synthetic compound structurally related to entactogens such as MDMA. Researchers study 5-MAPB for its serotonin-releasing properties, receptor affinity, and potential to model empathogenic effects in controlled lab environments. Unlike traditional substances, it has a benzofuran ring, making it structurally distinct.
What Is MDMA?
MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) is a widely researched entactogen, historically known for its stimulant and empathogenic effects. In scientific settings, MDMA serves as a reference compound for understanding serotonin release, dopamine interactions, and neurotoxicity risk. Its long history in both clinical and academic research makes it a benchmark against which new analogs like 5-MAPB are compared.
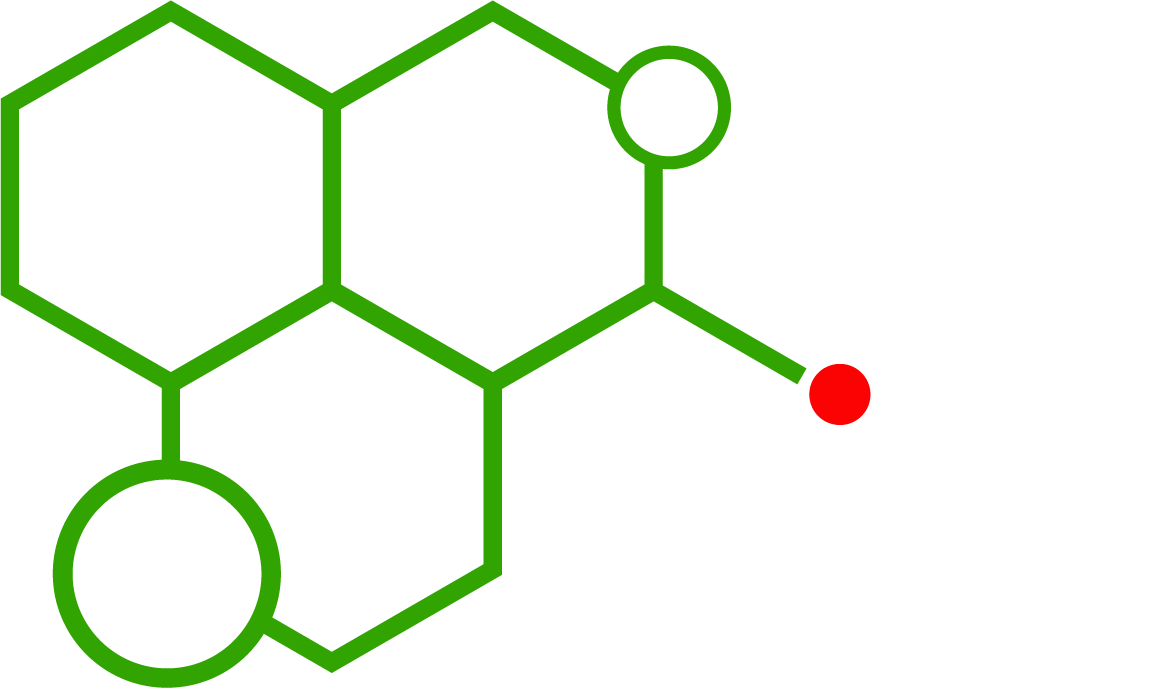
Chemical Structure: 5-MAPB vs MDMA
The structural differences between 5-MAPB and MDMA significantly influence their effects:
- 5-MAPB: Features a benzofuran ring, giving it slightly different metabolic stability.
- MDMA: Contains a methylenedioxy group on the phenyl ring, contributing to its distinct pharmacological profile.
These subtle changes alter receptor binding, half-life, and safety considerations during laboratory use.
Pharmacological Activity
Researchers investigating 5-MAPB vs MDMA note differences in pharmacological action:
- 5-MAPB appears to produce longer-lasting serotonin release in vitro compared to MDMA.
- MDMA is associated with higher dopaminergic activity, which contributes to its stimulant effects but also raises concerns about neurotoxicity.
These differences provide opportunities for comparative research in neurotransmitter systems and receptor selectivity.
Research Applications
In laboratory contexts, both substances are valuable but serve different purposes:
- 5-MAPB is studied for its potential as a research model in understanding entactogen-like activity without identical risk factors.
- MDMA is used as a baseline compound in psychopharmacological and toxicological studies, often compared with newer analogs.
Researchers often include other cathinones like 3-CMC or 2-MMC in broader structural-activity comparison studies.
Safety and Handling
When working with these compounds, strict safety protocols are essential. Researchers should:
- Consult Safety Data Sheets (SDS) before handling.
- Store compounds in sealed containers under controlled conditions.
- Use proper personal protective equipment (PPE) as outlined in Essential Protective Equipment for Chemical Researchers.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The legal status of both 5-MAPB and MDMA varies globally. While MDMA is classified as a controlled substance in many countries, 5-MAPB’s legal position may differ depending on jurisdiction. Researchers must comply with regulations set by agencies such as the DEA in the U.S. and the ECHA in Europe.
Conclusion
The comparison of 5-MAPB vs MDMA highlights the impact of small structural changes on pharmacological outcomes and research applications. Both compounds provide unique opportunities for studying serotonin and dopamine systems, with MDMA serving as a benchmark and 5-MAPB offering an alternative for comparative studies.
For high-purity 5-MAPB and other research chemicals, Maxon Chemicals supplies reliable compounds with full SDS documentation. Related reading includes:
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 
Add a Comment