Pure CBD: Research Uses Beyond Consumer Products
Pure CBD: Research Uses Beyond Consumer Products
Pure CBD Research Uses extend far beyond the consumer wellness market. While most people associate cannabidiol (CBD) with oils, gummies, and supplements, researchers study Pure CBD to explore its pharmacological properties, receptor interactions, and potential therapeutic effects in controlled laboratory environments.
What is Pure CBD?
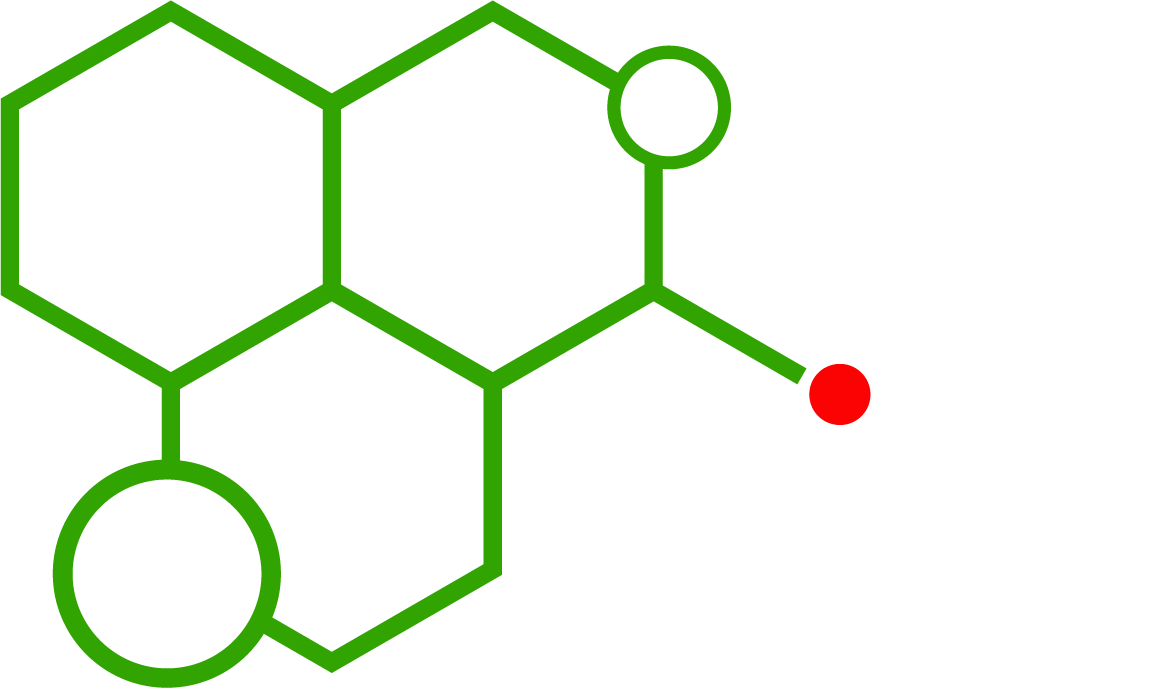
Pure CBD is cannabidiol in its isolated form, free from THC and other cannabinoids. Its chemical structure allows scientists to study its effects on the endocannabinoid system, including interactions with CB1 and CB2 receptors. This makes it a valuable compound for pharmacology, neuroscience, and toxicology research.
Pharmacological Research Applications
Researchers utilize Pure CBD for various laboratory studies:
- Exploring neuroprotective properties in models of neurological disorders.
- Investigating anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
- Studying receptor binding and signaling pathways in cellular assays.
By isolating CBD from other cannabinoids, scientists can better understand dose-response relationships and mechanism of action without interference from psychoactive compounds.
Analytical and Experimental Studies
In laboratory settings, Pure CBD is used to develop analytical methods, including chromatography, mass spectrometry, and NMR spectroscopy. These techniques allow researchers to quantify CBD concentration, study its stability, and assess interactions with other compounds. Comparative studies often include analogues or derivatives to examine how minor chemical modifications affect pharmacological activity.
Safety and Handling
Even though CBD is generally considered safe, laboratory handling requires adherence to SDS guidelines and proper protective equipment. Researchers also follow protocols for storage and degradation prevention, as outlined in shelf-life studies, to ensure sample integrity for reproducible results.
Comparative Studies with Synthetic Cannabinoids
Pure CBD is frequently compared with synthetic cannabinoids such as JWH-210 or 6-CL-ADBA to evaluate differences in receptor activity, toxicity, and metabolic pathways. These comparisons provide insight into how natural and synthetic compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system, supporting pharmacological research and drug development.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Pure CBD is generally less regulated than THC-containing compounds. However, researchers still need to comply with national and international guidelines, including recommendations from agencies such as the FDA and the EMA. This ensures research is conducted ethically, legally, and safely.
Conclusion
The study of Pure CBD Research Uses demonstrates its importance beyond commercial wellness products. Researchers can explore pharmacology, receptor mechanisms, anti-inflammatory properties, and neuroprotective effects using high-purity CBD. Comparative studies with synthetic cannabinoids like JWH-210 or 6-CL-ADBA further expand the understanding of cannabinoid pharmacology, making Pure CBD an invaluable tool in modern laboratory research.
For high-quality research-grade Pure CBD and related cannabinoids, visit Maxon Chemicals. Related resources:
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 
Add a Comment