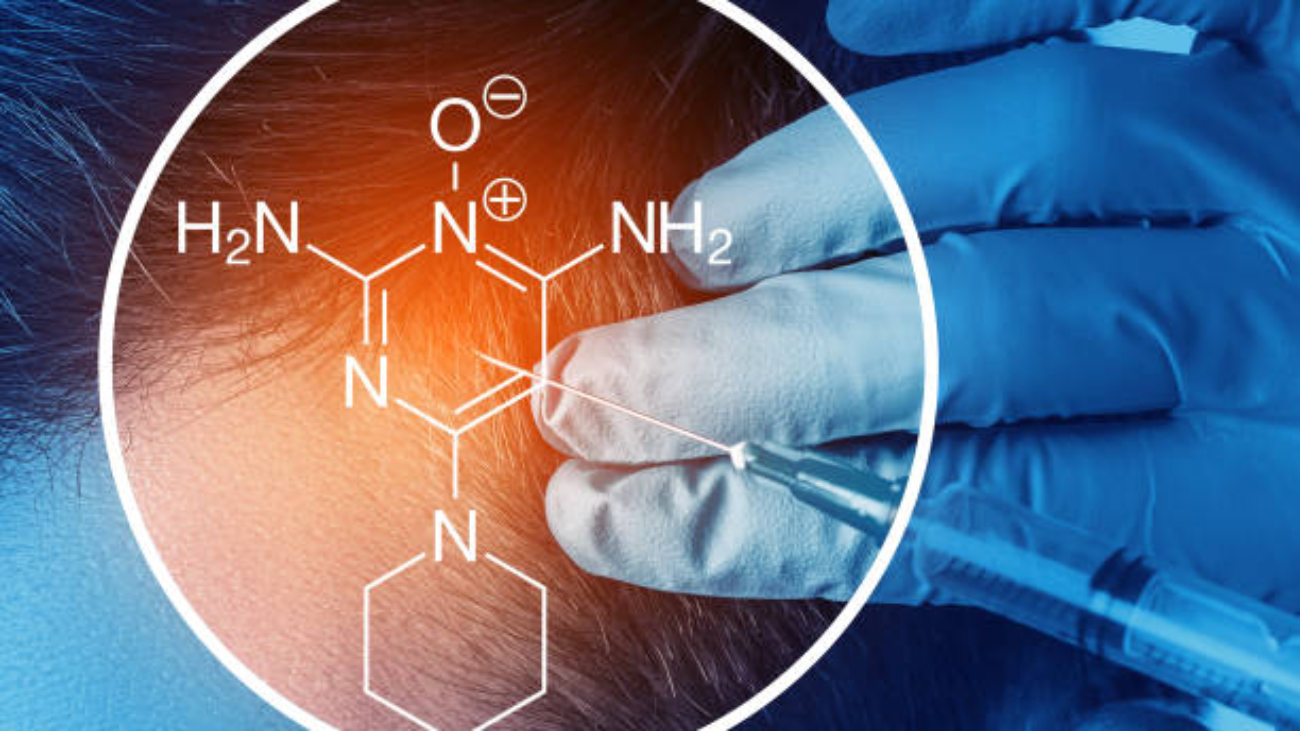
Introduction to Analytical Chemistry and Research Chemicals
Analytical Chemistry Research Chemicals: A Comprehensive Introduction
Analytical Chemistry Research Chemicals is a critical area for laboratories studying substances such as 3-CMC, 5-MAPB, and JWH-210. Analytical chemistry allows researchers to characterize chemical structures, assess purity, and detect impurities, ensuring both safety and data reliability.
Understanding Analytical Chemistry in Research
Analytical chemistry involves techniques that quantify, identify, and study chemical compounds. In the context of research chemicals, these methods help:
- Verify chemical identity and purity of compounds like 2-MMC and MDPHP.
- Develop safe handling and storage procedures.
- Support regulatory compliance through accurate documentation.
Common Analytical Techniques
Laboratories studying research chemicals use various analytical methods:
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Separates components for purity analysis.
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Identifies chemical structures and detects trace impurities.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): Provides structural insights for compounds like JWH-210 and ADB-BUTINACA.
- Infrared Spectroscopy (IR): Confirms functional groups within the molecule.
Applications in Research Chemical Studies
Analytical chemistry ensures reliable research outcomes by:
- Determining the concentration of synthetic stimulants and cannabinoids.
- Monitoring degradation products and shelf-life stability.
- Supporting toxicology and pharmacology studies.
- Assisting in regulatory compliance for controlled substances.
Safety Considerations
Proper lab safety is paramount when analyzing research chemicals. Best practices include:
- Using PPE such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats when handling compounds like Pure CBD or 5Cl-ADB-A.
- Following storage and stability protocols (storage guidelines).
- Maintaining up-to-date Safety Data Sheets (SDS).
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Analytical studies must comply with EU regulations such as REACH and CLP. Proper documentation ensures both ethical research and legal compliance.
Conclusion
Analytical Chemistry Research Chemicals provides the foundation for accurate, safe, and reliable research. By utilizing proper analytical techniques, maintaining rigorous safety standards, and sourcing high-quality compounds from trusted suppliers like Maxon Chemicals, laboratories can conduct meaningful scientific studies with confidence.
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty