MDPHP vs. α-PVP: Understanding Stimulant Analogs
MDPHP vs. α-PVP: Understanding Stimulant Analogs
In laboratory studies of synthetic cathinones, the comparison of MDPHP vs α-PVP is particularly important. Both compounds are stimulant analogs with similar chemical backbones, yet they differ in structural details, metabolic behavior, and potential research outcomes. Understanding these differences helps scientists evaluate their roles in psychostimulant studies.
What Is MDPHP?
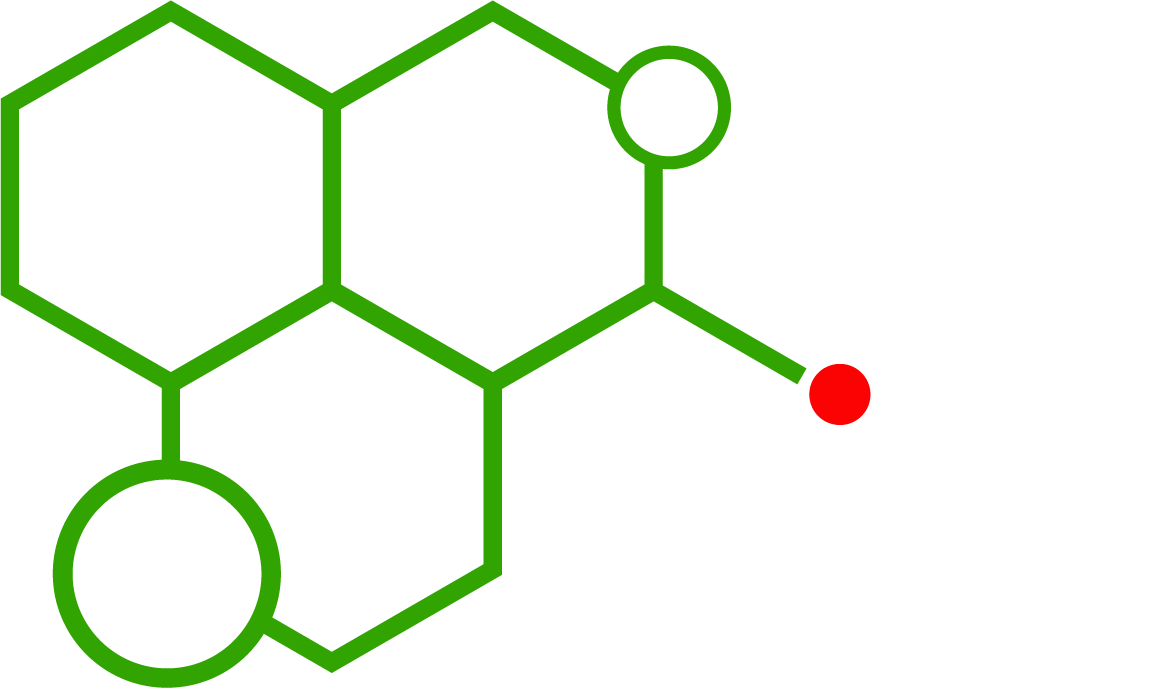
MDPHP, or 3′,4′-methylenedioxy-α-pyrrolidinohexiophenone, is a synthetic stimulant belonging to the cathinone family. Its distinguishing feature is the methylenedioxy substitution on the phenyl ring, which alters receptor binding and contributes to its psychostimulant profile. Researchers use MDPHP to explore stimulant pathways and structural-activity relationships in laboratory models.
What Is α-PVP?
α-PVP, or α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone, is another synthetic cathinone well-known for its strong stimulant properties. Unlike MDPHP, α-PVP lacks a methylenedioxy group, resulting in different pharmacological effects. Its simpler structure makes it a benchmark for comparison with more substituted analogs like MDPHP.
Chemical Structure: MDPHP vs α-PVP
While both compounds are pyrrolidinophenones, structural substitutions distinguish their profiles:
- MDPHP: Features a methylenedioxy group, increasing polarity and altering receptor interactions.
- α-PVP: Lacks this substitution, offering a less complex but highly active stimulant structure.
These differences influence not only their activity but also their metabolic stability and laboratory handling requirements.
Pharmacological Activity
Researchers investigating MDPHP vs α-PVP often compare how small modifications change activity levels:
- MDPHP: Reported to exhibit slightly longer-lasting effects in controlled in vitro research.
- α-PVP: Associated with faster onset and more intense stimulant activity in laboratory studies.
Both compounds contribute to the growing body of research on synthetic stimulants and their potential risks.
Applications in Research
In laboratory settings, MDPHP and α-PVP serve different but complementary purposes:
- MDPHP is often studied alongside methylated analogs such as 2-MMC to understand structure–activity relationships.
- α-PVP serves as a reference stimulant in comparative studies of pyrrolidinophenones.
Researchers may also include 3-CMC in comparative analyses to explore cross-family similarities.
Safety and Handling Considerations
As with all research chemicals, handling stimulant analogs requires strict safety measures. Researchers should:
- Consult Safety Data Sheets (SDS) before use.
- Store under airtight, temperature-controlled conditions as explained in Proper Storage Methods for Synthetic Cathinones.
- Use protective gear described in Essential Protective Equipment for Chemical Researchers.
Legal and Ethical Context
The legal frameworks for MDPHP and α-PVP differ internationally. Many countries classify α-PVP as a controlled substance, while MDPHP’s status may vary. Researchers should always follow regulations set by agencies such as the DEA in the United States and the ECHA in Europe. Conducting studies responsibly ensures both compliance and scientific credibility.
Conclusion
The comparison of MDPHP vs α-PVP highlights how subtle structural changes impact stimulant activity, safety, and laboratory utility. MDPHP’s methylenedioxy substitution sets it apart from α-PVP, making both valuable in comparative stimulant research. For researchers, choosing the right compound depends on the specific goals of their studies.
High-purity MDPHP and other stimulant analogs are available through Maxon Chemicals, with full SDS documentation to support safe laboratory use. Additional reading includes:
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 
Add a Comment