MMC: Exploring Its Role in Analytical Studies
MMC: Exploring Its Role in Analytical Studies
MMC in Analytical Studies is an important topic for researchers studying synthetic stimulants. MMC, including analogues such as 2-MMC, is used in controlled laboratory environments to investigate neurotransmitter interactions, pharmacology, and structure-activity relationships. Its chemical structure and properties make it valuable for analytical studies in chemistry and toxicology.
What is MMC?
MMC (Methylenedioxymethylcathinone or its common lab analogues like 2-MMC) is a synthetic cathinone used for research purposes. It acts as a stimulant in laboratory studies, influencing dopamine and serotonin pathways. Scientists use MMC to model the effects of other cathinones and better understand how minor structural changes can impact pharmacology.
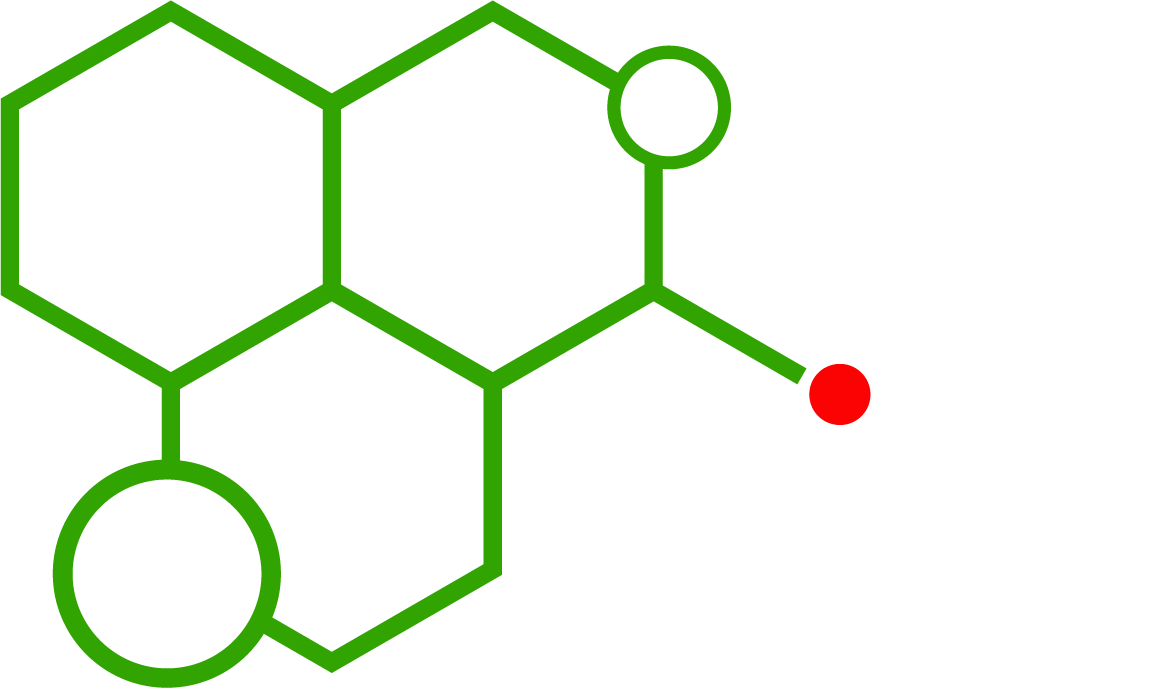
Chemical Structure and Key Properties
The molecular structure of MMC features a methcathinone backbone with variations depending on the specific analogue. Small substitutions, such as methyl groups, can affect binding affinity, metabolic stability, and potency. Comparing 2-MMC with 3-CMC provides insights into how structural analogues influence chemical behavior and analytical detection.
Applications in Analytical Research
Researchers utilize MMC in analytical studies for several purposes:
- Studying neurotransmitter activity and stimulant mechanisms.
- Comparing synthetic cathinones in controlled lab environments.
- Developing detection methods for forensic and pharmacological research.
Techniques such as chromatography, mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are commonly employed to analyze MMC and its analogues.
Safety and Laboratory Handling
While MMC is useful for analytical studies, it must be handled safely. Researchers should follow guidelines outlined in Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and use appropriate protective equipment. Proper storage, as described in storage protocols for synthetic cathinones, ensures compound stability for reliable analytical results.
Comparative Studies
In research, MMC is often compared with other stimulants like MDPHP and 3-CMC to assess differences in potency, receptor interaction, and metabolism. These comparative studies provide critical insights into the effects of minor structural modifications on chemical behavior and toxicological profiles.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
MMC and its analogues are regulated in various jurisdictions. Researchers must ensure compliance with laws governing synthetic cathinones, including guidelines from the DEA and the EMA. Proper authorization ensures safe, legal, and ethical laboratory research.
Conclusion
The study of MMC in Analytical Studies highlights its importance in understanding synthetic stimulants, receptor interactions, and analytical methodologies. By investigating MMC alongside analogues like 2-MMC and 3-CMC, researchers gain valuable insights into structure-activity relationships, pharmacology, and toxicology while maintaining high laboratory safety standards.
For high-quality MMC and other synthetic cathinones for research purposes, visit Maxon Chemicals. Related reading:
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 
Add a Comment