ADB-BUTINACA: Its Growing Popularity in Research Labs
ADB-BUTINACA: Its Growing Popularity in Research Labs
ADB-BUTINACA Research Uses have gained attention among scientists studying synthetic cannabinoids. This potent compound allows researchers to investigate receptor binding, pharmacological effects, and structure-activity relationships (SAR) in controlled laboratory settings. Unlike consumer-focused cannabinoids, ADB-BUTINACA is primarily used for scientific research and analysis.
What is ADB-BUTINACA?
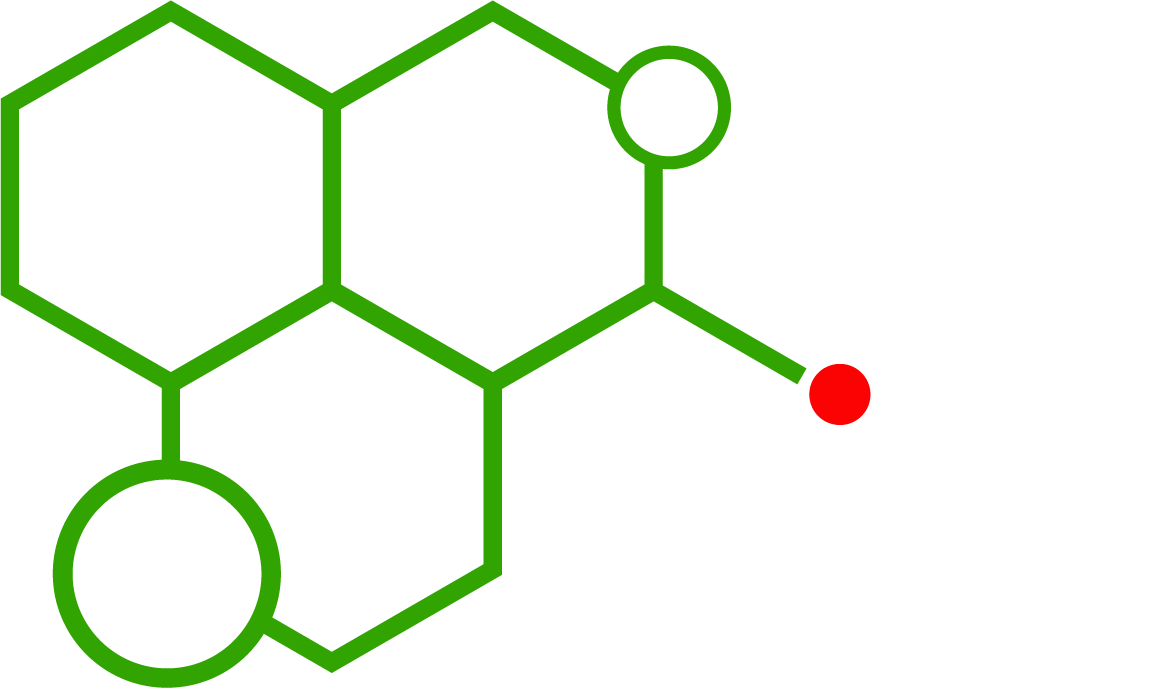
ADB-BUTINACA is a synthetic cannabinoid known for its high affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors. Its chemical structure includes an indazole core and a tert-butyl substituent, which significantly influence potency and receptor selectivity. Researchers compare ADB-BUTINACA with other cannabinoids like 5Cl-ADB-A and JWH-210 to study the effects of structural modifications.
Chemical Structure and Properties
The unique structure of ADB-BUTINACA contributes to its potent pharmacological profile. Laboratory studies focus on how its indazole and tert-butyl groups affect receptor binding, metabolism, and potential toxicity. Comparative analysis with compounds such as 6-CL-ADBA highlights the role of minor chemical modifications in synthetic cannabinoid behavior.
Laboratory Applications
Researchers utilize ADB-BUTINACA for a variety of purposes:
- Studying CB1 and CB2 receptor interactions.
- Analyzing pharmacokinetics and metabolic pathways.
- Investigating structure-activity relationships (SAR) among synthetic cannabinoids.
These studies help develop a deeper understanding of potency, toxicity, and receptor selectivity in synthetic cannabinoids.
Safety and Handling
Proper laboratory handling of ADB-BUTINACA is essential. Researchers should consult Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and use appropriate protective equipment. Storage protocols, similar to those for other synthetic cannabinoids, ensure sample integrity and reliability in experimental studies.
Comparative Research Studies
Comparing ADB-BUTINACA with compounds like 5Cl-ADB-A, JWH-210, and 6-CL-ADBA helps researchers understand differences in receptor affinity, potency, and metabolic stability. These comparative studies provide critical insights for pharmacological and toxicological research.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
ADB-BUTINACA is a controlled synthetic cannabinoid in many jurisdictions. Researchers must follow local and international regulations, including guidelines from the DEA and EMA, to ensure safe and legal laboratory research practices.
Conclusion
The study of ADB-BUTINACA Research Uses highlights its importance in understanding synthetic cannabinoid pharmacology, receptor interactions, and structure-activity relationships. By comparing it with compounds such as 5Cl-ADB-A, JWH-210, and 6-CL-ADBA, researchers gain valuable insights into potency, receptor selectivity, and safety. Strict adherence to laboratory safety and regulatory compliance ensures effective and ethical research outcomes.
For high-quality research-grade ADB-BUTINACA and related synthetic cannabinoids, visit Maxon Chemicals. Related resources:
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty