Researching Alternatives: Pure CBD vs. Synthetic Cannabinoids
Researching Alternatives: Pure CBD vs. Synthetic Cannabinoids
The discussion of Pure CBD vs Synthetic Cannabinoids is a central topic in modern chemical research. While cannabidiol (CBD) from natural sources has gained significant popularity for its potential therapeutic uses, synthetic cannabinoids like JWH-210, 6-CL-ADBA, and ADB-BUTINACA offer controlled, lab-designed alternatives. Researchers compare these categories to explore pharmacological profiles, safety considerations, and possible applications.
What is Pure CBD?
Pure CBD (cannabidiol) is a naturally occurring cannabinoid extracted from hemp or cannabis plants. It is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not cause intoxication like THC. Studies have suggested potential benefits in areas such as anxiety relief, inflammation reduction, and seizure management. Because of its natural origin and relatively low toxicity, Pure CBD has become a reference point for cannabinoid research.
What Are Synthetic Cannabinoids?
Synthetic cannabinoids are lab-manufactured compounds designed to mimic or alter the activity of natural cannabinoids at CB1 and CB2 receptors. Examples include 5Cl-ADB-A and JWH-210. Unlike CBD, which works as a mild modulator, many synthetic cannabinoids act as full agonists, producing stronger and less predictable effects. These differences make them valuable in controlled studies exploring receptor activation and toxicological profiles.
Structural Differences
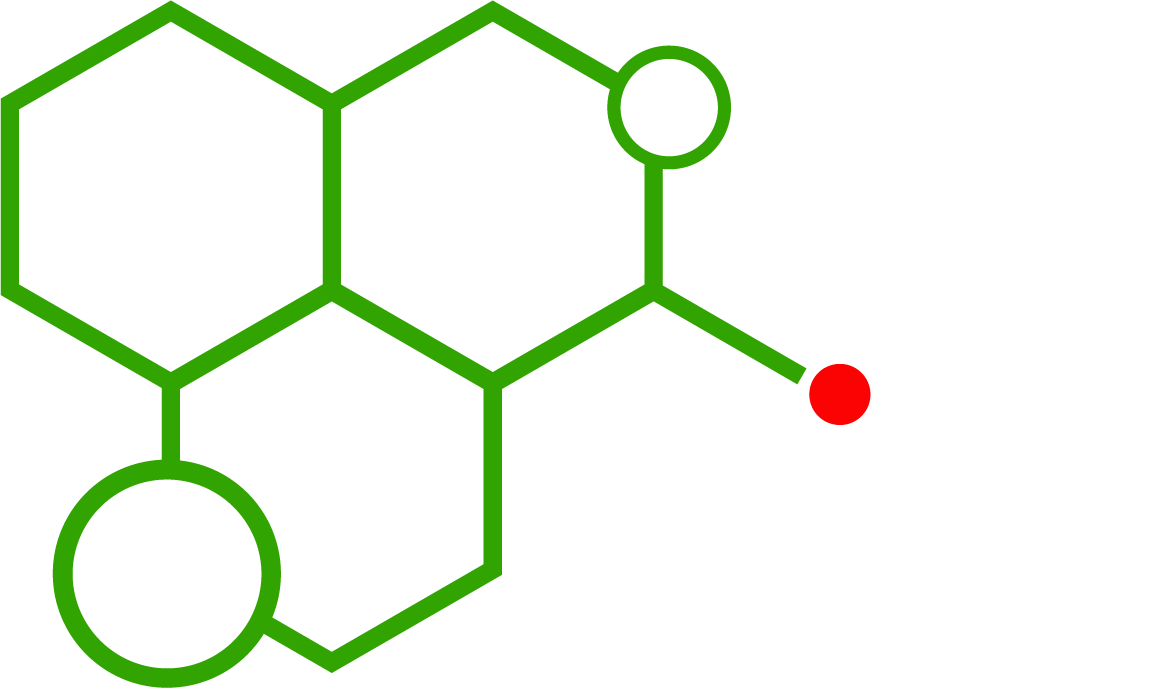
In the debate of Pure CBD vs Synthetic Cannabinoids, structure is a defining factor. Pure CBD is a terpenophenolic compound derived from plants, while synthetic cannabinoids like ADB-BUTINACA are indazole-based chemicals. These differences allow researchers to test how small structural modifications influence receptor binding and potency.
Pharmacological Effects
Pure CBD typically acts indirectly on cannabinoid receptors, moderating their activity without directly binding as a strong agonist. Synthetic cannabinoids, on the other hand, often act as full agonists at CB1 receptors, which may result in more pronounced effects. This makes them useful for research into neurological pathways and receptor sensitivity, but it also introduces higher safety risks compared to CBD.
Safety Considerations
When comparing Pure CBD vs Synthetic Cannabinoids, safety emerges as a crucial difference. Pure CBD has been extensively tested and is widely regarded as safe, even at high doses. Synthetic cannabinoids, however, may have unpredictable side effects due to stronger receptor activity and limited toxicity data. Researchers handling substances like 6-CL-ADBA or 5Cl-ADB-A must follow strict Safety Data Sheet (SDS) guidelines and use protective equipment to minimize risks.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape
The legal status of Pure CBD differs widely from that of synthetic cannabinoids. CBD products are legal in many regions, particularly when derived from hemp with low THC content. Synthetic cannabinoids, however, are often subject to stricter regulations due to safety concerns and classification as controlled substances. Researchers must remain compliant with organizations such as the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) when sourcing and handling these chemicals.
Applications in Scientific Research
Both Pure CBD and synthetic cannabinoids are valuable in laboratory studies, though for different reasons:
- Pure CBD: Used in therapeutic research, neuroprotection studies, and as a baseline comparator for synthetic analogs.
- Synthetic Cannabinoids: Designed for receptor binding studies, analog development, and toxicological modeling.
The contrast of Pure CBD vs Synthetic Cannabinoids provides insight into how structural variations influence pharmacological outcomes.
Conclusion
The exploration of Pure CBD vs Synthetic Cannabinoids underscores the balance between natural safety and synthetic innovation. While Pure CBD remains a well-documented, relatively safe compound for research, synthetic cannabinoids such as JWH-210 and ADB-BUTINACA allow researchers to test hypotheses about receptor mechanisms, potency, and chemical modifications. Together, these categories help advance cannabinoid science in meaningful ways.
For research-grade cannabinoids and other compounds, explore the range of products at Maxon Chemicals. Related reading includes:
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 
Add a Comment